About Our Study
Introduction
The waste management according to global definition is the collective efforts made to collect, transport, dispose or recycle and efficiently monitor waste products. There are four major categories of waste which are municipal solid waste, industrial waste, agricultural waste and hazardous waste. Some of the disposal methods used in the global research are open dumping, landfilling, composting, incineration, and for radioactive waste cases, it will be a permanent land burial method. According to the Malaysian Investment Development Authority (MIDA), there are also four major types of waste generated in Malaysia which are industrial, commercial, domestic, and agricultural. The systems used in Malaysia for waste management are 3R, composting, incineration, bio-energy, sanitary landfilling and illegal dumping. The management of construction waste is currently underdeveloped in Malaysia, with the only waste management practiced on the construction site being the sorting of debris into recycling bins. The decision to implement sustainability in waste management is largely influenced by finances, as well as by inadequate awareness and a shortage of competent people. A literature review on GIS application in waste management at UTM (Universiti Teknologi Malaysia) reveals that there is a growing interest in using GIS to improve waste management systems. On the use of GIS in waste management at UTM, several case studies have been done. For instance, Abdul Rahman et al(2018) 's study suggested a waste management plan to increase the effectiveness of waste collection and disposal by using GIS to examine the spatial distribution of waste generation and disposal on campus.Our project is to develop an application by using GIS application to propose recommendations for improving waste management practices to achieve sustainable and efficient waste management in UTM.
Problem Statement
UTM is facing the challenge of managing its waste effectively while also promoting sustainability. The current waste management practices and facilities may not be optimized for full efficiency and sustainability , leading to potential negative impacts on the university environment and resources.
Objectives
- To identify the problem of the current waste management system by conducting the quistionaire and site visit.
- To conduct an optimum path analysis by gathering all appropriate parameters regarding the waste management.
- To map the location of the dumpsters and the optimum route of the waste truck within the UTM’s area.
- To find out ways on how to make the current waste management system more effcient
- Population density
- Travel distance
- Average speed based on the population density
- Travel time
- Add more dumpsters throughout UTM permanently
- Waste Reporting app for students & staffs
- Waste collection only after office hours nearby faculty as it causes distress among students because of the loud noises that takes place
- Adaptive collection scheduling for big events that happen in UTM and temporary dumpsters nearby the location
Study area
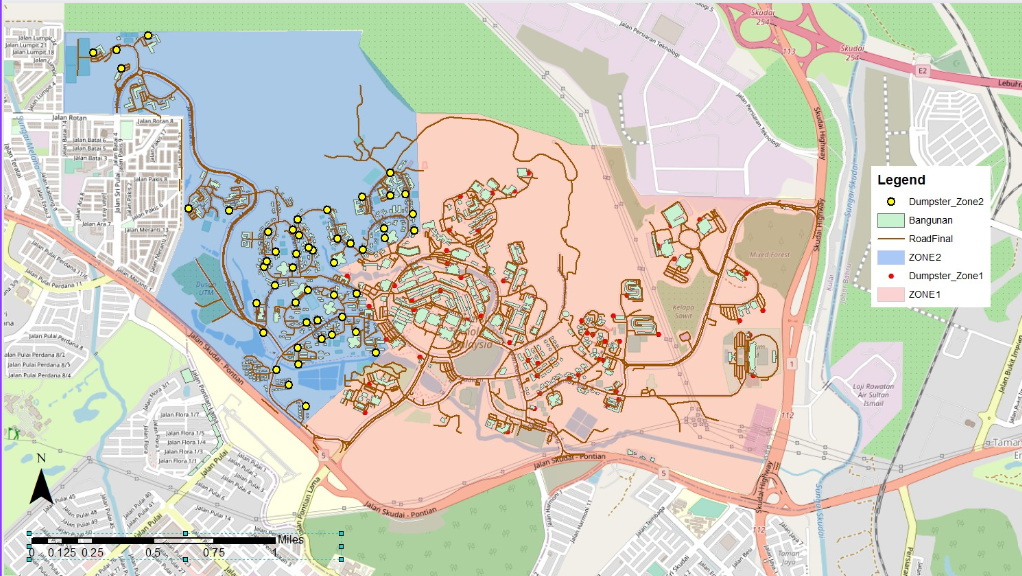
The campus is seperated into 2 zones for easier management
Stakeholder : PHB UTM
Waste Collection Process

GIS Application Used
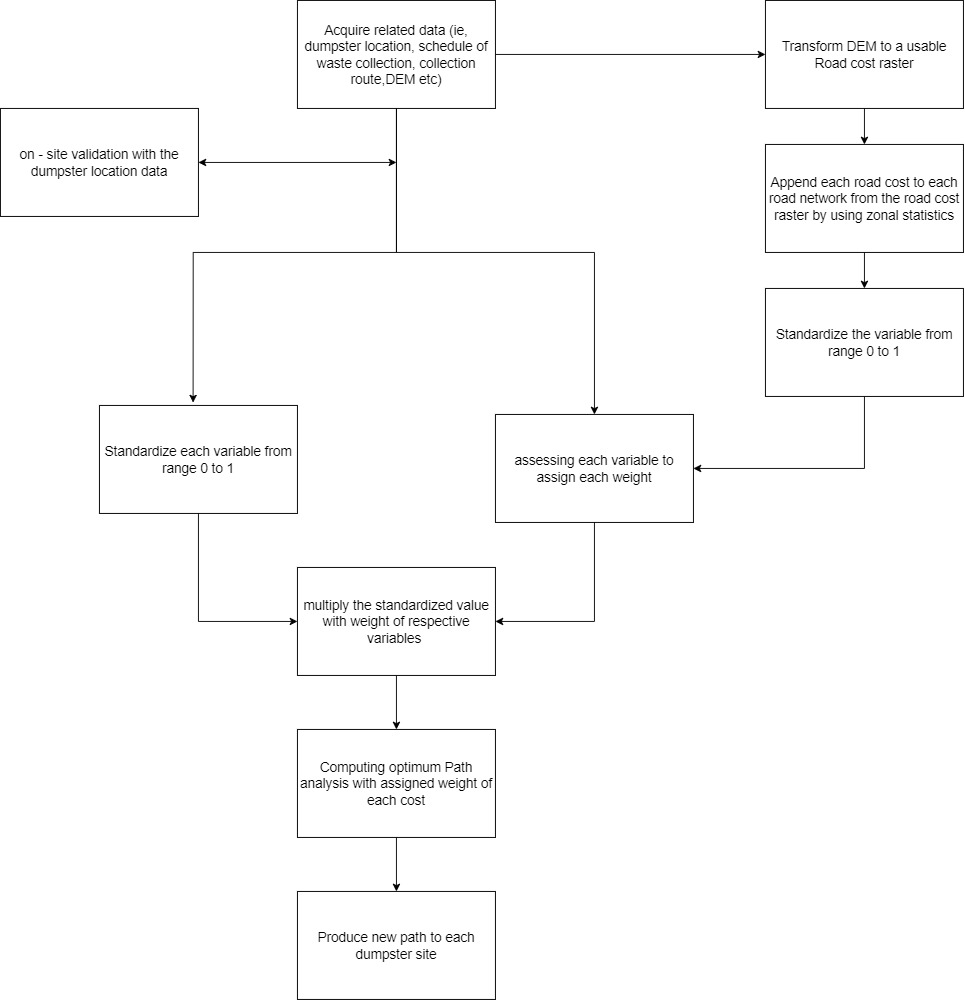
Optimum Path Analysis
The optimal path analysis is aligned with the objective of this project which is to analyze the most optimal route in which the garbage truck will traverse through it based on the parameter;
Flowchart of Optimum Path analysis process
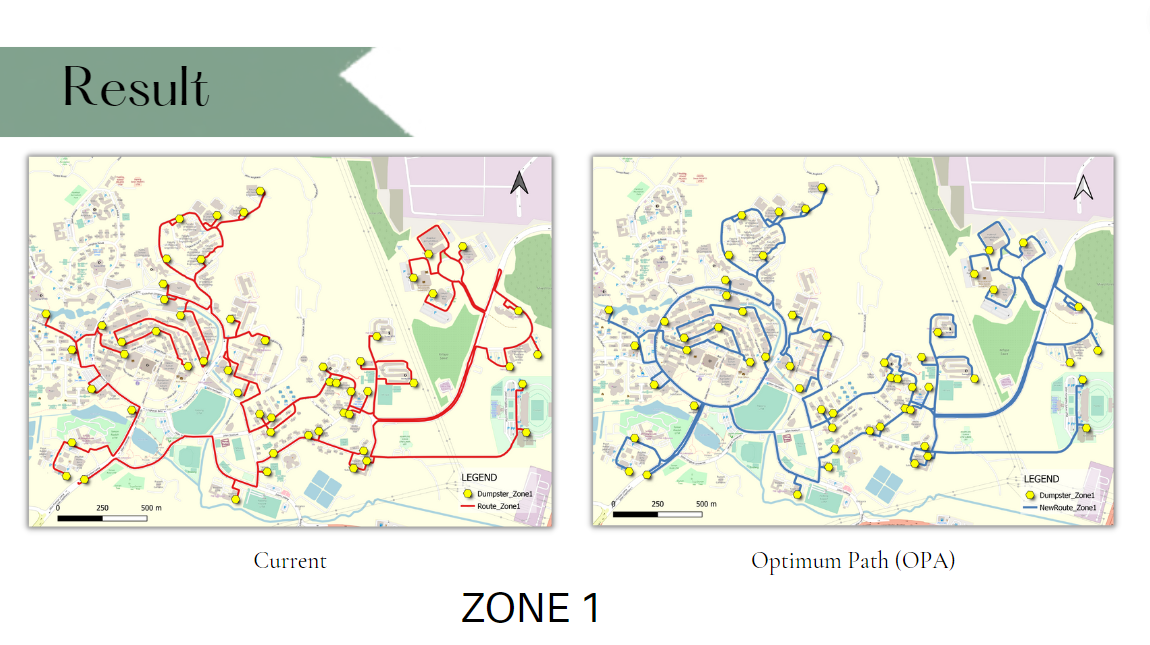
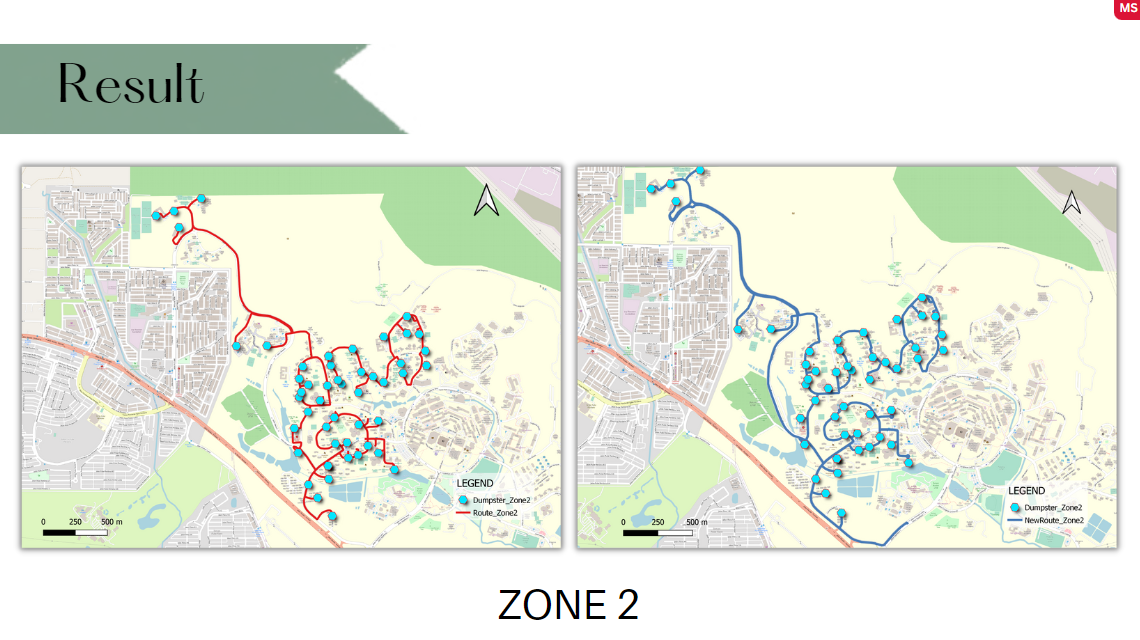
Ways to make the current waste management system more effective and efficient
Conclusion
Our analysis of the optimal path helps to find the optimal route for the truck's distance travelled based on a few parameters such as population density, travel distance, average speed and travel time of the truck. To provide services that are more efficiently by reducing the time spent travelling between collection points.
UTM is gearing towards a zero waste campus especially in administration and academic